Selecting the right drip irrigation tubing can ensure optimal water efficiency and plant health. Drip irrigation or trickle irrigation, is a type of micro-irrigation system, dripping water onto the soil at very low rates (2-20 liters/hour) from a system of small-diameter plastic pipes fitted with outlets called emitters or drippers . The goal is to place water directly into the root zone and minimize evaporation. Drip irrigation systems distribute water through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. Depending on how well designed, installed, maintained, and operated it is, a drip irrigation system can be more efficient than other types of irrigation systems, such as surface irrigation or sprinkler irrigation. Drip irrigation, via the use of quality polyethylene drip tubing, is both an economical and efficient way to irrigate most forms of plant life. Reading this buying guideline will guide you through the realm of drip irrigation tubing. If you are looking for one of these products, follow this comprehensive buying guideline for choosing the best drip irrigation tubing based on your need.

1. Key Considerations When Choosing Drip Irrigation Tubing
A number of factors must be considered for selecting the finest drip irrigation tubing. These are some crucial factors that shall guide you in choosing the best drip irrigation tubing:
1.1. Purpose and Application
To begin with, it is important to understand the application of drip irrigation tubing and your purpose for buying them. Drip irrigation is an efficient and economical way to water your yard and garden. Used commonly in drier areas of the country, drip irrigation is becoming more popular in the Northeast. Unlike other forms of irrigation, such as sprinklers that are only 65-75% efficient, drip irrigation 90% efficient at allowing plants to use the water applied. And, it reduces runoff and evaporation. Drip irrigation applies the water slowly at the plant root zone where it is needed most. This can be ideal for both homeowners and professional farmers. Drip irrigation involves placing tubing with emitters on the ground alongside the plants. The emitters slowly drip water into the soil at the root zone. Because moisture levels are kept at an optimal range, plant productivity and quality improve. In addition, drip irrigation:
Drip irrigation can deliver 1 to 4 gallons of water per hour to a landscape bed, and there is no drift, which is what happens when wind carries water dispersed from an irrigation system to areas that do not need water (your sidewalks, walkways and parking lots). Drift wastes water.
Drip irrigation installation does not require excavating and rarely disrupts the integrity of a landscape bed during installation. Tubing is weaved throughout the area requiring watering. Therefore, drip irrigation systems can be moved and are not permanent like conventional irrigation systems (involving spray heads, pop-up heads, etc.).
With drip irrigation, water is delivered directly to the ground’s surface rather than being sprayed up and out over an area. This direct application of water yields water savings.
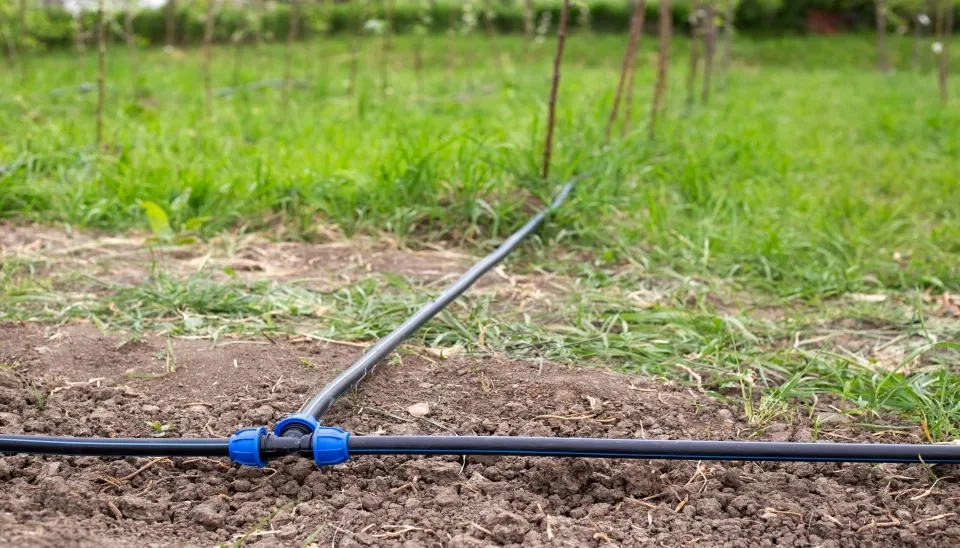

1.2. Emitter Spacing
Emitter spacing is an important factor when selecting a drip irrigation because it directly impacts the distribution of the water. They are small holes along the tumbling that emit the water at a certain rate. The emitted spacing can be determined by the type of plants being irrigated, their root zones, and the layout of the garden or field. For dense vegetation and crops, closer emitter spacing is vital to ensure proper watering to the root zone. For trees with extensive root zones, a wider spacing is better. If the emitter spacing is too wide, the water can not reach the zone properly, which can lead to stress for the plant. On the other hand, if the emitter spacing is too dense, it can result in water loss, and over saturation and root rot. Soil type can also affect the emitter spacing. For example, soils with higher permeability require closer emitting space because water can spread out more quickly. However, finer soils like clay that can retain water for longer periods can have wider emitter spacing. Therefore, for optimal efficiency, you need to consider all the factors, such as plant type, soil properties, irrigation method, and available water.
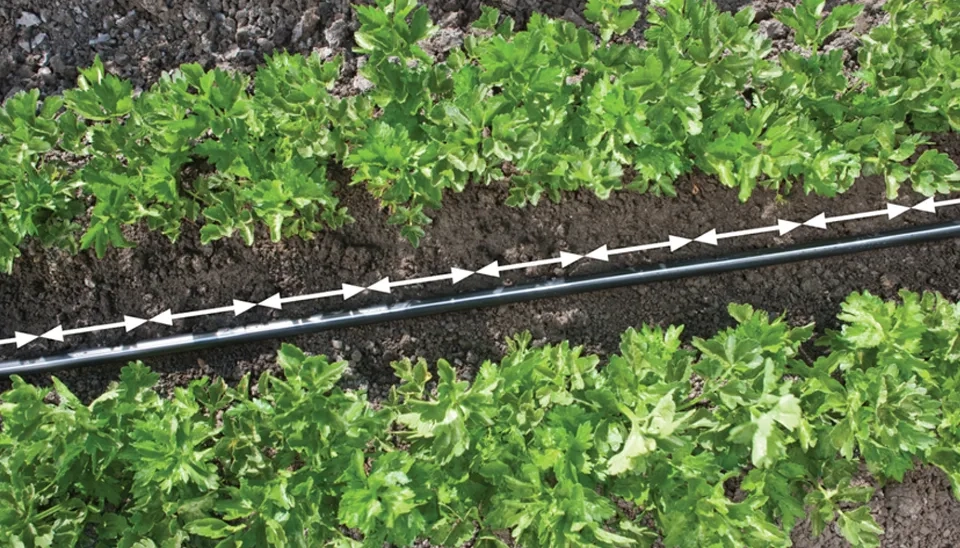

1.3. Flow Rate
Flow rate is a determining factor because it quantifies how much water is delivered to the plants during a specific period. This feature can be defined by emitter design and is usually measured in gallons per hour (GPH) or liters per hour (LPH). A suitable flow rate can guarantee optimal plant growth while maintaining water usage as low as possible. For example, for small plants, a low flow rate (such as 0.5 to 1 GPH) can be used, while for larger plants with higher water demand, a higher flow rate (up to 2 GPH or more) is needed. Moreover, flow rate is directly linked to the water pressure because emitters are designed to work at a specific pressure. Therefore, if the water pressure becomes too low, the flow rate for the emitters might be insufficient. On the other hand, high pressure can make the emitters work too quickly, leading to flooding and root zones as well as wasting water. Therefore, it is essential to select a flow rate that correlates with the pressure. Another important factor is making sure that flow rate is distributed uniformly, which means that all emitters must emit most have the same flow rate at the same time to ensure uniform coverage. Thus, tumbling with high length can cause a decrease in flow. In addition, consider the type of soil, as it can directly influence the flow rate. For example, a sandy solid that can move the water quickly needs a lower flow rate to prevent flooding. While clay soils that need time to absorb water need a higher flow rate to make sure that the water reaches the root zone.
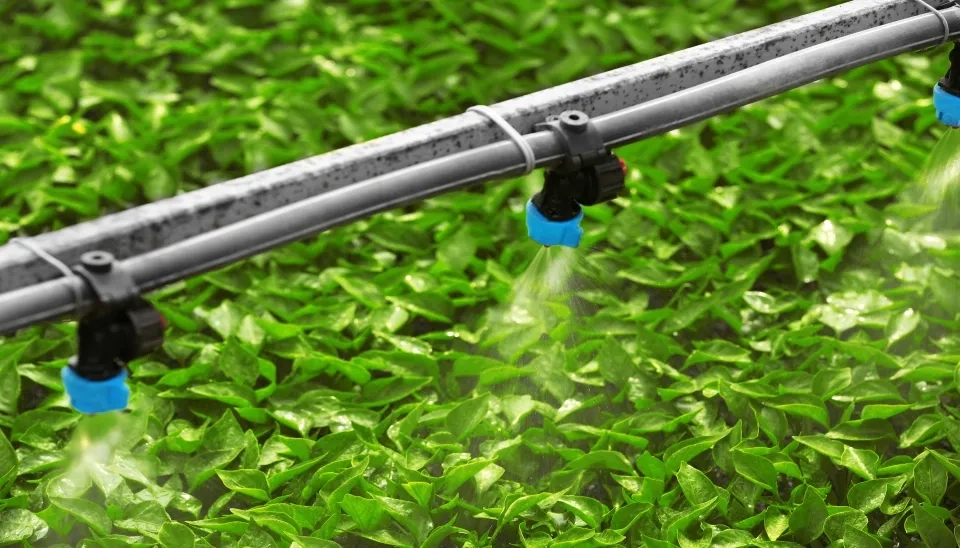

1.4. Material
Drip tubing is a polyethylene tube with emitters placed along the plants. The emitters release the water from the drip tubing. Drip tubing and emitters come in various types and diameters depending on your needs. Polyethylene is the most common material due to its flexibility, resistance to UV degradation, and cost-effectiveness. This makes PE tubing especially suitable for both temporary and permanent installations, especially where flexibility and ease of installation are important. This is the usual case in vegetable gardens and row crops. Orbit Irrigation One Stop Outdoor 1/4-Inch Drip Irrigation Tubing (100 ft) is one of the products on the market with Polyethylene (PE) material. This irrigation tubing contains 6 inches of pre-inserted emitter spacing and is used with 1/4" fittings. This product is resistant to fertilizers and chemicals that people usually use in gardening and farming. This drip irrigation tubing can be easily installed due to its flexibility. It is also compatible with most 1/4" fittings. This product is well-designed to prevent leaking issues and blowouts. The emitters deliver equal flow at a wide range of operating pressures.

Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is another popular material that is more rigid than PE. PVC pipes play a crucial role in drip irrigation systems. These pipes are known for their durability, affordability, and ease of installation. PVC pipes are commonly used for sub-main lines due to their ability to withstand pressure and resist corrosion. Highly recommend PVC or PE for your main line runs. The greater ability of PE to cope with incidents and issues of this kind makes it a better choice for long-term irrigation projects, whereas the ease and simplicity with which PVC piping can be installed may make it a better choice for smaller projects that need to be completed at speed. One of the drip irrigation tubings in the market that is made of PVC is Furnrubden Drip Irrigation. Moreover, for applications that need additional durability, reinforced tubing is available. Their strength has been elevated by materials like nylon or polyester fibers to tolerate harsh environments and slopes. This type of tumbling is usually used in complex irrigation systems where high pressure is needed. Moreover, these tumblings have resistance to bursting and puncturing.

1.5. Tubing Size and Length
The size of the drip irrigation tubing is essential to deliver the right amount of water to the plants. Tubing size refers to the diameter of the hose, which can influence flow rate and pressure. Probably the most popular size is 1/2” poly tubing, since this is the most commonly used size for drip systems. Often, it serves as a mainline in small- and medium-size gardens. It can also be used as a header or branch line off a bigger mainline for larger growing operations. Gardena 1346-20 is one of the products in the market with 1/2” diameter. Moreover, if the tubing size is too narrow for the pressure, the water flow can be restricted. Therefore, understanding the pressure rating and flow rate is vital. Another factor that is important is the length of the tube. Total area that you need to cover and number of plants or rows that require watering are the main factors that impact the tubes’ length. If the tube is too long, the water will distribute unevenly, especially in low-pressure systems. To avoid this, you can install a pressure regulator or shorter tubing. Moreover, the length of a single drip tube should not exceed 200 feet from the point where water enters the tube. You will need to stake the tubing to keep it from moving.
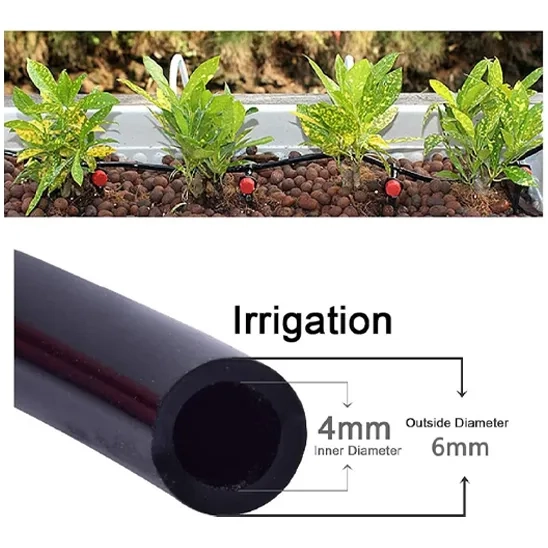

1.6. Type
Drip irrigation tubing is classified into emitter tubing, blank tubing, soaker hoses, microtubing, and pressure-compensating tubing, each serving specific irrigation needs. Emitter tubing has built-in emitters at regular intervals for precise water delivery, making it ideal for row crops and landscaped areas. Soaker hoses gradually seep water along their length, ensuring even moisture distribution, particularly in small gardens and flower beds. Micro Tubing provides targeted watering by connecting mainlines to individual plants, making it suitable for container plants and tight spaces, though it is prone to clogging. Pressure-compensating tubing maintains a consistent water flow regardless of pressure variations, making it ideal for sloped landscapes and large irrigation systems.
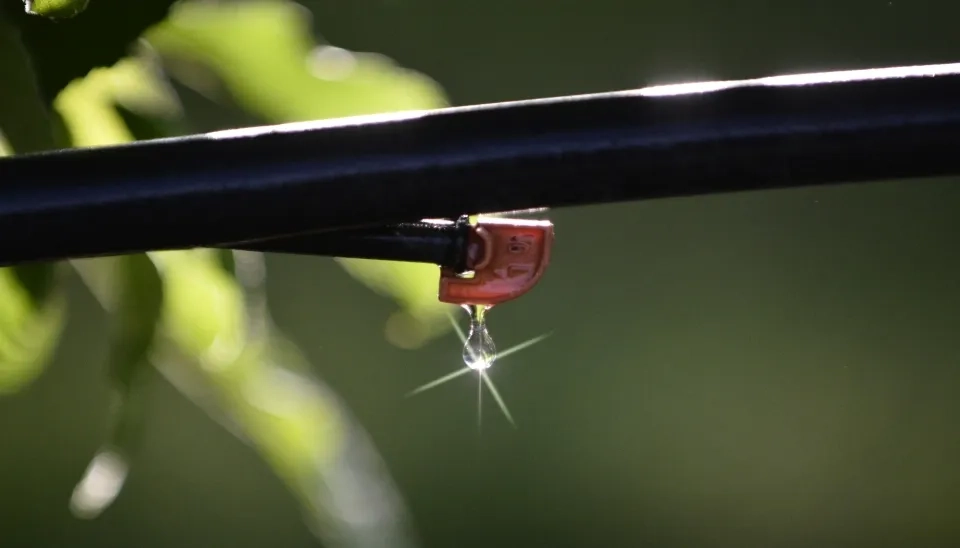

1.7. Maintenance
Check filters and emitters on a regular basis to ensure they are functioning properly.
Irrigation systems will only operate well if properly maintained. This is particularly relevant for drip irrigation systems, as problems are not easy to identify before they become a problem, and emitting devices are very small compared to other irrigation methods, meaning blockages can more readily occur. The most common problems with drip irrigation systems are emitter clogging, deterioration of dripper components or mismanagement of system pressures. Regular maintenance and monitoring are the best ways to prevent & treat Irrigation system clogging. Over time, system performance will decline to some degree in all drip systems regardless of management, but it is important to minimize this decline through maintenance and monitoring. Systems that are regularly flushed, cleaned, have adequate filtration and are initially well designed should maintain an acceptable level of performance. Even with a good filtration system, blockages to drip systems can occur, and it is important to regularly flush mains, submains, and laterals. Flushing these three components in this order is an important practice that generally doesn’t receive the attention it requires. Depending on water quality, it is recommended to give the piped system a complete flush before the first irrigation of the season, several times during the season and again at the end of the season. Monitoring the water quality during flushing will determine whether flushing is occurring frequently enough. As a guide, flush three times a season when irrigating with clean water and at least once every fourth irrigation with dirty water. Automatic flushing valves can be an option installed at the end of each lateral. These valves purge when the laterals are filling up at the start of each irrigation and may provide a suitable backflushing option if frequent flushing is required. Irrigators have had mixed results with this method of flushing, and it is recommended to regularly remove these valves and manually flush the laterals to ensure that an adequate flush has occurred.

1.8. Product Ratings
This buying guide outlines the essential factors to consider when selecting the best drip irrigation tubing. By following these criteria, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your needs. Additionally, this buying guide suggests checking Waterlyst’s Bayesian ranking to consider user reviews and comments, as these can provide valuable insights from those who have already used the product. It’s also important to consult our article, "10 Best Drip Irrigation Tubing for Watering Your Plants," which serves as a great starting point for narrowing down your options. The article ranks the products based on Bayesian ranking methods, offering a more reliable comparison than traditional methods. As highlighted in this buying guide, the MIXC 1/4-inch Drip Irrigation Tubing (50-foot) ranks first, made from high-quality, low-density polyethylene. This tubing is durable and weather-resistant, making it suitable for long-term use in a variety of environments. Whether buried underground or placed on the surface, it is highly flexible and easy to install in gardens, farms, or landscaped areas. Compatible with various emitters, misters, and fittings, the MIXC tubing is ideal for small, tight planting areas with curves and switchbacks. It also conserves water by saving up to 70% and reducing overspray, ensuring that your plants receive efficient watering without wasting water on surrounding soil. Be sure to consider these features when making your decision, as detailed in this buying guide.
1.9. Customer Service
This buying guide emphasizes the importance of ensuring that your drip irrigation tubing purchase comes from a company that offers solid support. A responsive manufacturer can significantly enhance your experience by assisting with the installation process, ensuring the accuracy and effectiveness of the device. Another crucial element highlighted in this buying guide is the availability of warranties, which provide peace of mind in case the device encounters any issues. Many companies, as mentioned in this buying guide, offer free repairs or replacements during the warranty period. This buying guide also recommends looking for companies that offer post-warranty support with easily accessible spare parts. When issues arise, it's essential to be able to contact customer service through live chat, call, or email. Furthermore, some companies create online forums or social media groups, as described in this buying guide, where customers can share their experiences and discuss common issues with the product.

2. Assessing Your Specific Needs Before Buy
Your needs are the first priority when buying suitable drip irrigation tubing; it is vital to evaluate your particular needs when selecting a product that adequately fulfills your requirements. This includes evaluating requirements and allocating a reasonable budget. The above steps can ensure that you will make an informed decision by considering all the factors while fulfilling your usage objective.
2.1. Calculate Your Requirements
Before buying drip irrigation tubing, it is essential to calculate several factors to make an informed decision. Before anything else, you need to calculate the area you plan to irrigate. Measure the length and width of the garden or landscape to perform these calculations. If the shape is irregular try to break it into small segments. Moreover, it is important to identify the flow and pressure rate of your current system to select the best drip irrigation tubing compatible with it. Each drip emitter will have its flow rating, usually given in liters per hour. Multiply the number of emitters (per plant) by the flow rate per emitter to get the total flow rate. The total flow rate will help ensure that the tubing is capable of moving the volume of water required without excessive loss of pressure or to prevent under-watering. Emitter spacing is another element to consider, which should be determined based on your plant's types and positions. If the emitters are too close together, more water can be delivered to the root zone , but more tubing is needed. Finally, calculate the total amount of tubing needed for your garden or landscape based on the emitter spacing. The tubing must cover all the rows and plants to ensure water delivery. Some extra tubing is needed to connect the mainline to the distribution lines and any obstacles.

2.3. Set Your Budget
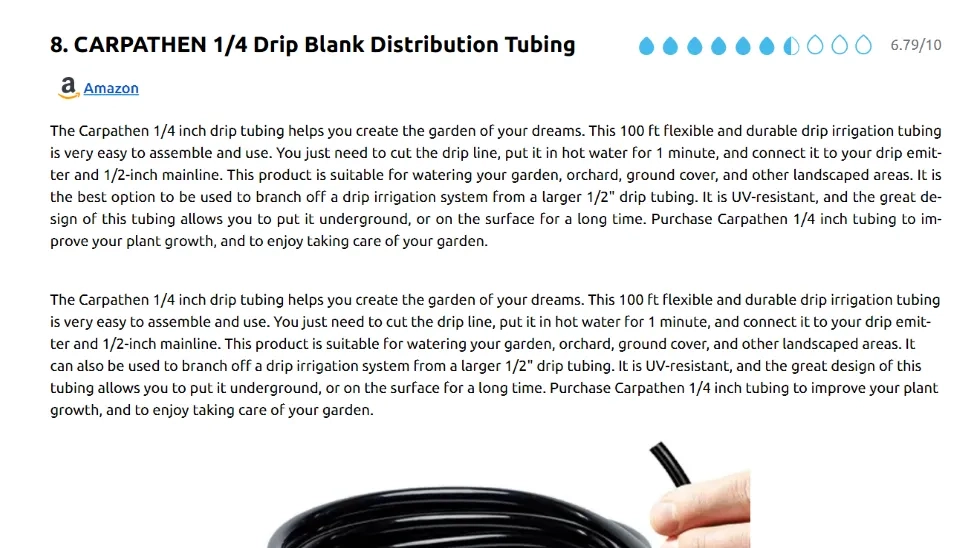
Drip irrigation tubing can have different prices based on the flow rate, material and brand, and by determining the budget , you can narrow down your options. Basic drip tubings, which are non-pressure compensating, typically have a price range of $0.10 to $4 per foot. They are cheaper and suitable for small gardens or relatively flat areas. For example, CARPATHEN 1/4 Drip Irrigation Tubing costs $4 per foot. This type of tubing is usually used for simple, low-pressure systems. Drip tubing with pressure compensation has a price of $0.30 to $6 per foot. This type can maintain pressure along the tube and is ideal for uneven terrain or variable water pressure. Ein Bird ET63918-100 - 1/2 in tubing has pressure-compensating with a price of $2.68 per foot. is a Moreover, Soaker hose tubing has a price range of $0.20 to $5 per foot, which is ideal for even gardens and landscapes. Its price can vary based on the material and wall thickness. Emitters can have prices of $0.05 to $0.50 each, depending on their flow rate and type. For example, HouseUp Emitters can cost $0.07 each. The total cost for a drip irrigation system will depend on the area that needs to be covered, how complicated the setup is, and what quality of material is used. The budget may permit the use of high-quality tubing, which may demand a higher initial investment but provides superior performance and a longer lifespan.

3. Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Drip Irrigation Tubing
To avoid any mistakes, it's important to understand certain key factors when choosing drip irrigation tubing. Many gardeners rush into installing drip irrigation without proper planning and research. They need to understand their plants' water requirements, their garden layout, or the flow rate of their water source. This lack of knowledge can result in serious issues, such as uneven watering, system overloading, or using the wrong irrigation products. Planning ahead can make a significant impact. Learn how much water your plants need, check your water pressure vs. flow rate, and sketch your garden's layout. Then, pick the right tubing, emitters, and fittings. One of the most common mistakes is to overlook flow and pressure rate. Tubes, based on their size, can handle a certain amount of pressure. If the pressure is too low, water cannot be delivered to all the crops. Another mistake is not considering the crop positions for emitter spacing. Emitters should not be too close or too far from each other to maintain their performance. Moreover, the tubing material must be selected based on your application. PE tubing can be formed easily, making it ideal for winding around trees and other obstacles, while PVC pipes are known for sturdiness, a long life span, and pressure resistance. Thus, you cannot use PVC for irregular shapes that require winding. Furthermore, it is important to take into account the environmental condition of your garden and landscape because extreme temperatures and freezing can cause tubing to crack or deteriorate, decreasing longevity.

Another common mistake is not installing filters, because many think that water from a clean source can be acceptable without filtration. Municipal water systems, wells, or tanks can introduce debris into your irrigation lines, and using organic fertilizers can worsen the situation by leaving residues. This debris can clog emitters and reduce or even stop the water flow. Therefore, installing a filter is an effortless and effective way to protect your system. All tubing can experience some kinking. Tubing with a large inside diameter (ID) is more prone to kinking, especially when bent sharply or twisted. Kinks can block water flow, causing uneven watering and leaving the plants thirsty. Kinks usually happen when you try to make sharp turns without using proper fittings like elbows. Therefore, when buying connectors and fittings, you should double-check the compatibility of your tubing. The dimensions of the tubing should match those of adapters, connectors, and fittings to prevent potential kinks. Many gardeners prefer elbow fittings for smooth 90-degree turns in pipes, tubing, or hoses. Mainline tubing may kink on corners, so every turn must have an elbow fitting.
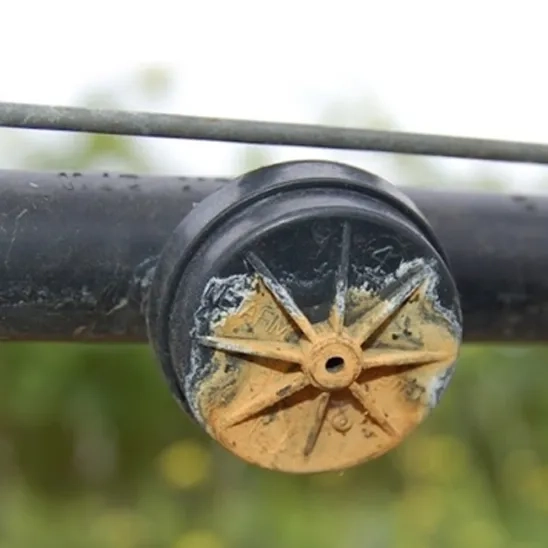

4. Checklist for Choosing the Best Self-Water water planters
Have you recognized the best material based on your application? (e.g., PE, PVC, rubber, etc.)
Have you recognized the emitter spacing is needed?
Have you identified the required flow rate and pressure based on your system?
Have you calculated the length required for your garden or landscape?
Does the expense align with your budget while maintaining the overall requirements and keeping the right balance between expense, features, and durability over time?
Are the materials durable and aligned with the environment in which you plan to use the products?
Have you searched for the customer service and availability options? (e.g., warranty, professional assistance , return policy, rapid delivery, packaging, free monitoring service and responsiveness)
Have you searched product rankings and reviews to ensure reliability? (e.g.,Bayesian Rank, buying guides, reviews, comments, etc.)
5. Conclusion
This is an ultimate buying guide for buying drip irrigation tubing, with a focus on important features such as flow and pressure rate, material, emitter spacing and others. This buying guide is for homeowners who are interested in buying the best drip irrigation tubing suited for their applications. Secondly, these buying guidelines also mention some of the errors that people commit while buying drip irrigation tubes, for instance, overlooking the flow and pressure rate, overlooking environmental conditions, and not giving priority to the specific crop involved. This buying guide covers a range of drip irrigation tubes. Last but not least, this buying guideline provides a checklist to help people make decisions and ensure that they do not overlook any crucial points before buying. This checklist will guide them to make the most efficient decision so it is compatible with their requirements presently and can be made suitable for the future. According to these recommendations mentioned in this buying guide, they can select a system that facilitates proper water usage, improves water quality, and even reduces maintenance and expenditure.
