As the years go by, not only is the water shortage becoming more and more serious, but also the water demand has become increasingly high. Meanwhile, agriculture and irrigation are responsible for more than 70% of water usage (FAO, 2020). Therefore, it is essential to decrease this percentage and use new strategies for irrigation.
Drip irrigation has a significant advantage in controllable precision and is known as the most efficient water-saving technique, which is used all over the world (Pitt et al., 1990). In agriculture, surface irrigation, where water flows through the crops, is the traditional method of irrigation, which causes huge water loss. This is because the water must flow through the sand, where it may evaporate, before reaching its destination. Drip irrigation is a technique of micro irrigation, which helps to reduce water loss and increase crop productivity by using each drop for its purpose. This technique is an advanced system that allows direct watering to be made through the crop. In contrast with traditional irrigation methods, drip irrigation makes sure the water gets into the roots of the plants (Appukuttan & G M, 2019).
Now that the importance of the drip irrigation system is clarified, in this study, the mechanism of this system and its components will be described and give essential knowledge to the readers.

1. Application of Drip Irrigation System
This method of irrigation is widely used in farms, commercial greenhouses, urban agriculture and rooftop gardens, water-sensitive areas, and home gardens. Additionally, in arid areas where water scarcity is high, particularly for crops and trees, the usage of drip irrigation systems becomes increasingly common. For crops such as vegetables, soft fruits (bananas, mangoes, watermelons, papayas, etc.), and high-value crops, drip irrigation plays an important role (Jarwar et al., 2019). Different types of drip irrigation systems are available to reduce water usage and improve crop yields in various areas and conditions. These systems are divided into four main groups, which are 1) surface drip irrigation, 2) subsurface drip irrigation, 3) in-line drip irrigation, and 4) micro sprinkler irrigation or online drip irrigation (Çetin & Kara, 2019).
To get more information about these systems, their application, and their impacts on agricultural irrigation, you can check the other article, which explains those topics.
2. Components of Drip Irrigation System
The components of a drip irrigation system in agriculture are divided into three main categories, which are (Razali et al., 2016): 1) water source and pump; 2) filtration unit; 3) network of pipes.
Each of these categories includes some components and equipment that will be introduced in the following paragraphs.
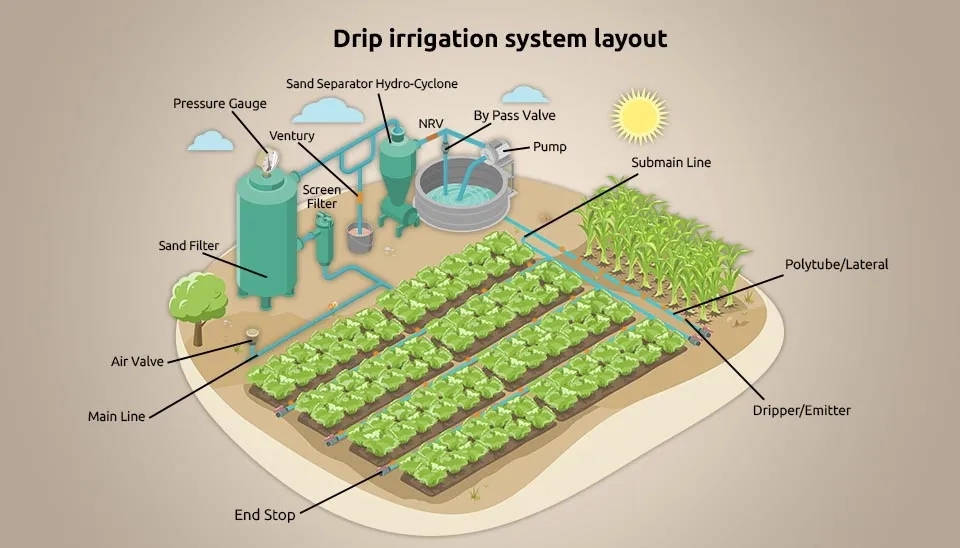
2.1. Water Source and Pump
An open well, a borewell, or a canal could be the water source. Meanwhile, depending on the availability of water and areas to be irrigated, a pump may be installed. The pumps are composed of a power unit, as well as a centrifugal deep submersible pump and accessories. It is good to know that high efficiency is the most important requirement to consider while designing and selecting pumps for drip irrigation systems (Shareef et al., 2019).
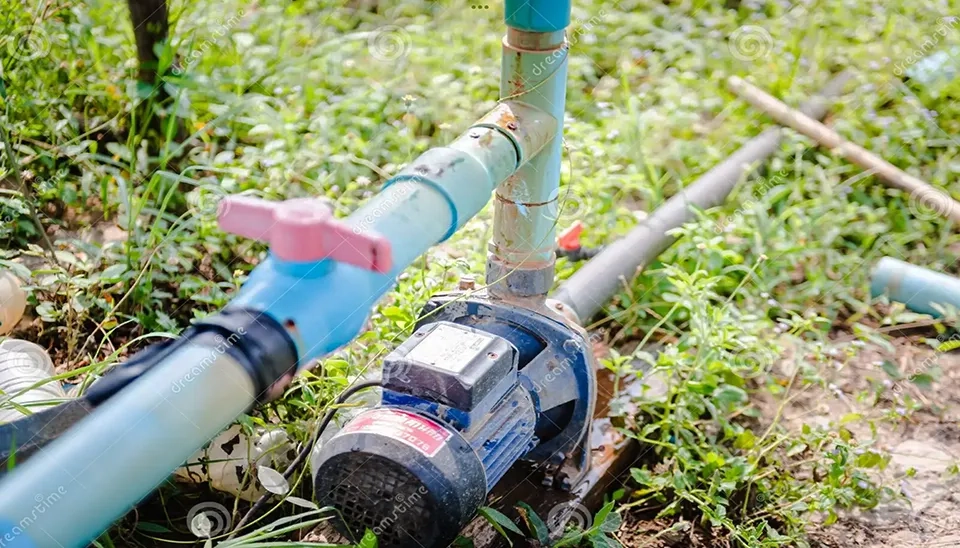

2.2 Filtration Unit
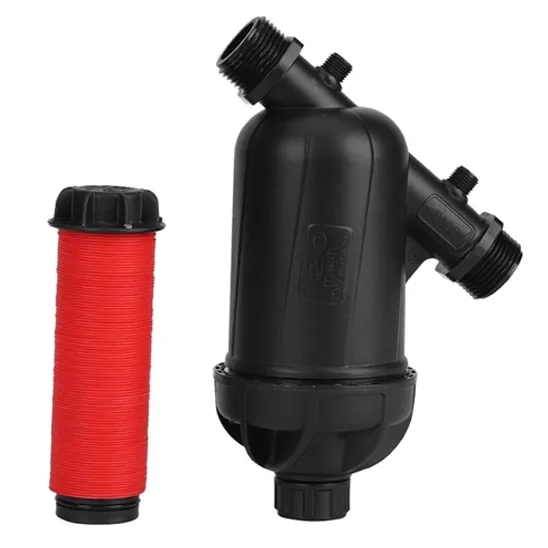
The main component of the drip irrigation system is the filtration unit, which consists of filters, pressure gauges, valves, and, in some cases, fertigation tanks. The drip system filters the water before it enters. There are many types of filters, such as hydro-cyclone filters, sand or media filters, and screen or disc filters, which can be used for municipal water or wells (Marr & Rogers, 1993).
Despite the high costs, this technique is reliable and simple to clean. However, it must be pointed out that sand filters are critical for open water sources or any surface source of water (Abdiyev et al., 2023).
Moreover, to maintain the continuity of the system with the correct pressure, pressure gauges are critical for monitoring the operation of compressed irrigation systems (Kaushik et al., 2023).
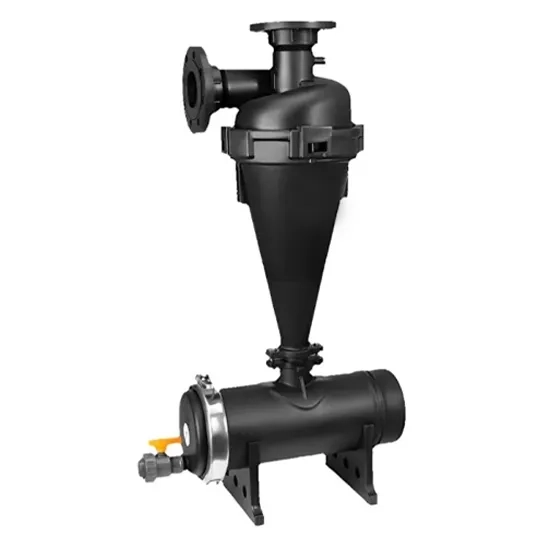

Disc filters are filtering machines comprising stacked plastic discs with tiny grooves that clog up water particles. They operate under pressure and are easy to clean through a backflushing system, making them efficient and maintenance-free. Disc filters are employed in drip irrigation systems to filter out fine sediments and organic matter to avoid clogging of the emitters.

Sand filters are water treatment appliances that use beds of sand for removing suspended solids and water contaminants. They function on a principle of letting water trickle slowly through the sand bed, in which the particles are caught between grains. Sand filters are used as a preliminary filtration step to protect downstream filters and prevent the clogging of emitters in irrigation system.

2.3 Network of pipes
The network of pipes in drip irrigation systems consists of main lines, sub-main lines, laterals, emitters or dippers, and control valves. The size and length of these components depend on the design of the system. Meanwhile, the selection of emitters is based on the amount of water demand in crops (Arbat et al., 2010).
Main line: The main line is considered to have a remarkable pipeline diameter within the irrigation system, which delivers water under proper hydraulic conditions to flow speed and loss of friction to transfer the water to the sub-main line (URI, 2023). It must be considered that the pipes used in this component are made of different materials, such as PVC, galvanized light steel, and black High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) which are buried permanently. Additionally, the size of the pipes depends on the farm area and the design of the drip irrigation system (Benouniche et al., 2014).
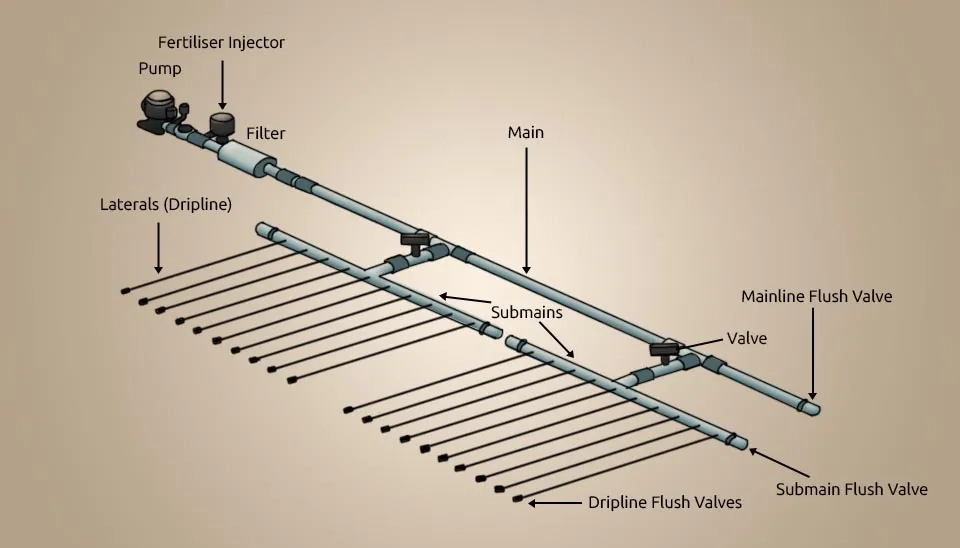
Sub-main line: To distribute the water, used for irrigation, to different plots of field level, the sub-main lines are made of the same type as the main line pipes but with a smaller size. These smaller pipes extend from the main pipe to various plots at the field level (Bisconer et al., 2014).
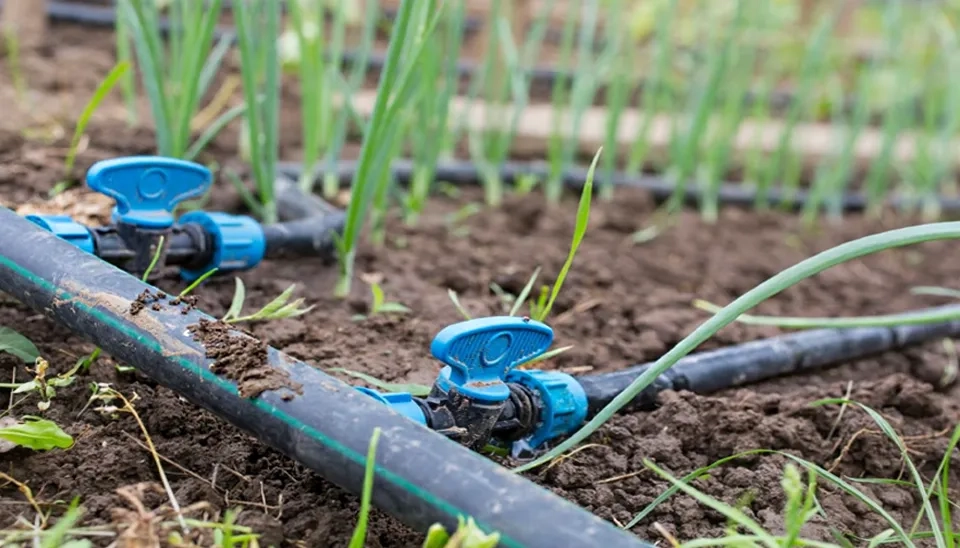

Lateral: To convey water from the sub-main line to the emitters and then to the root zones of the plant, the laterals are used, which are made of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) tubing available in black color. These lines can be placed as both surface and subsurface lines as well (Molina-Martínez et al., 2009).

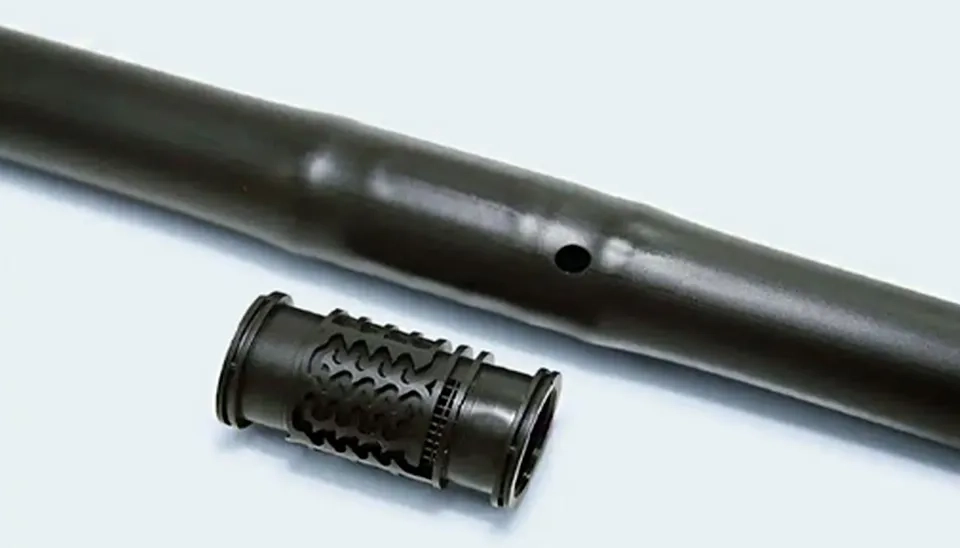
Emitter: To improve soil moisture without losing a significant amount of water due to evaporation, wind, and runoff, the emitters are considered the main part of this irrigation system as they transport small amounts of water directly into the plant root zones (Kuper et al., 2009). Drip emitters are categorized into 2 different groups based on their installation place, which are on-line emitters and in-line emitters. Each of these categories has several types of emitters according to their operating features.
In-line emitters are integrated directly into the dripline tubing at set intervals, making sure water is evenly distributed all the way down the line. They’re especially handy for row crops and plants that are closely spaced, offering a hassle-free setup and dependable performance.
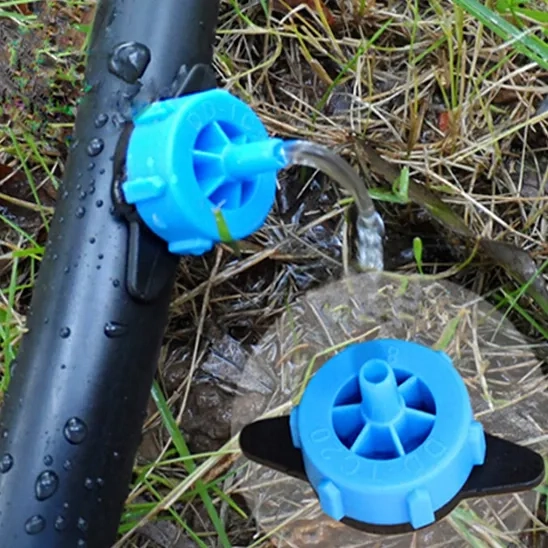

Internet emitters, by contrast, are individual drippers directly attached to lateral pipes within a drip irrigation system. They send water straight to the bottom of each plant, making them ideal for orchards or crops spaced quite far apart. The best news? You simply need to reposition them or regulate the flow rate to match the specific watering needs of the particular plant.

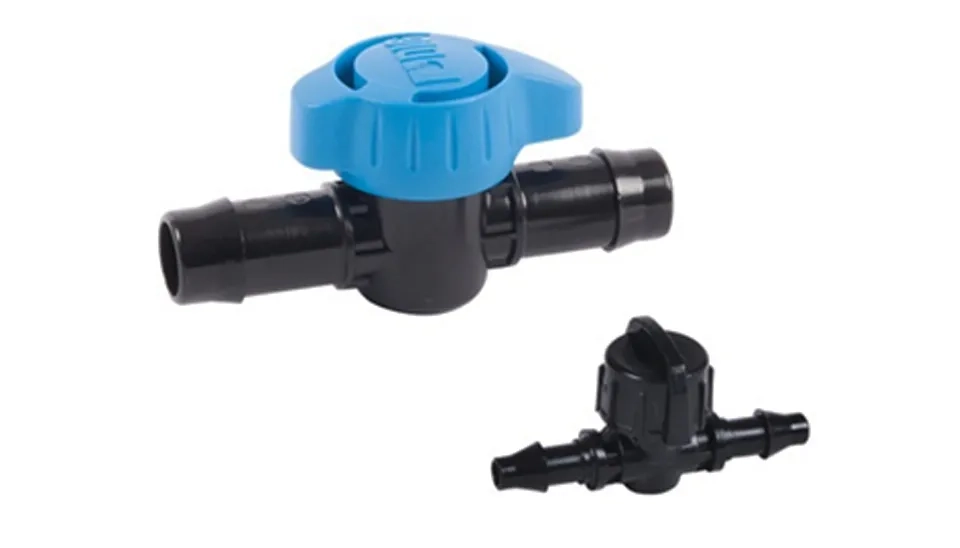
Valves: They are one of the most important components of drip irrigation systems due to their responsibility for controlling and checking the flow of water in the system (Powel et al., 2013).

3. Advantages of Drip Irrigation System
Since drip irrigation is considered an efficient method of agricultural irrigation, it must have different benefits in many aspects. Therefore, some of the most important advantages and benefits are going to be introduced (Arshad, 2020; Tagar et al., 2012).
Saving more than 50% of water usage due to low evaporation loss
Capability of irrigating bigger areas
Decreasing soil erosion
Decreasing weed growth
High constant water distribution
Accommodating different shapes and fields
Easy installation and less labor cost
Obtaining higher yields of good quality products
Decreasing energy cost due to lower pressure operation compared to other methods
Capability of using saline water or recycled water for irrigation
Enhancing seed germination
Increasing water infiltration
4. Disadvantages of Drip Irrigation System
Despite the benefits of drip irrigation systems, it's important to acknowledge their drawbacks. Hence, it is necessary to know these disadvantages to evaluate the efficiency of this method for each case. Some of the main disadvantages of drip irrigation systems are (Pei et al., 2014; Jayant et al., 2022):
High primary cost
Requirement of high skill in designing and installing
Emitters and laterals clog
Damaged components, causing water leakage
Salinity problems in root zones due to little leaching fraction
Difficulty in checking efficient moisture distribution
Affecting soil content as a result of plastic degradation by sunlight
5. New Trends In Drip Irrigation System
Nowadays technology has been developed in different subjects and drip irrigation is one of them. New trends and technologies have merged with drip irrigation systems and created new methods. The purpose of these new methods and systems is to improve the efficiency of drip irrigation and prevent some of the drawbacks associated with usual drip irrigation. Therefore, in the following paragraphs, some of the most useful new trends in drip irrigation systems are explained.
Fertigation: The combination and usage of fertilizers with irrigation water utilizing drip irrigation systems is the definition of fertigation. In today's agricultural irrigation, fertigation has become more usable by irrigators. In other words, locally managed irrigation systems such as drip irrigation and fertigation result in increased water and fertilizer efficiency (Cetin & Akalp, 2019).
Automated drip irrigation system: Automated or intelligent drip irrigation systems are developed to overcome the problems caused by human actions in the operation of usual drip irrigation systems. In this trend, the control of the drip irrigation process has been equipped with automation tools using a specific program that considers the water demands of different plants. Automated drip irrigation systems would allow farmers to use water more effectively in agricultural irrigation, which would allow them to take full advantage of available water resources (Majidov et al., 2023).
Smart irrigation system: Smart irrigation methods have improved the efficiency of agricultural irrigation by including wireless communication systems, updated control techniques, and monitoring equipment for a reliable irrigation schedule. This method adjusts the irrigation according to soil and weather conditions so that farmers can meet their demands with a new water-saving technique (Abedin et al., 2017). The main components of this method consist of smart sensing, energy harvesting, the importance of an Internet connection, real-time irrigation scheduling, and the Internet of Things (IoT) (Gamal et al., 2023).
6. Conclusion
A drip irrigation system is one of the most efficient modern methods for irrigation in agriculture. The study explained how this system helps farmers to reduce their water consumption and improve the quality of their products. It is essential for irrigators and household gardeners to understand this system and its components in order to design or select the most suitable equipment for their specific field conditions. It is concluded that this technique can merge with new technologies for better operation and a higher percentage of water savings. All in all, studying different irrigation methods widens our knowledge and helps us to avoid old, inefficient irrigation methods and apply better systems in our agricultural irrigation systems.
7. Quiz
To test the material learned in this article, you are invited to answer the quiz raised by the text.