Water pollution is the hidden nemesis threatening our very existence. Rapid population growth, urbanization, and the expansion of industries all contribute to the significant release of pollutants into the atmosphere. Among various contaminants, water pollution stands out as a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. This type of pollution not only poses risks to human health but also harms the environment and negatively impacts agriculture. Ensuring access to safe and clean drinking water has become a critical global concern. According to UN predictions, by 2025, approximately 50% of the world's population will live in regions where water scarcity poses a serious challenge. To achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation, it is crucial to adopt sustainable water treatment practices to provide safe and clean water (The UN 2022).
There are several water treatment practices that can be categorized into physical, chemical, and biological methods, such as membrane separation, photo-electrochemical oxidation, and activated sludge processes, respectively. However, it is important to note that not all water treatment methods are sustainable, as some suffer from issues like high energy consumption, excessive costs, and significant waste production. Sustainable water treatment practices, on the other hand, aim to utilize cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and socially acceptable techniques (Nishat et al. 2023).
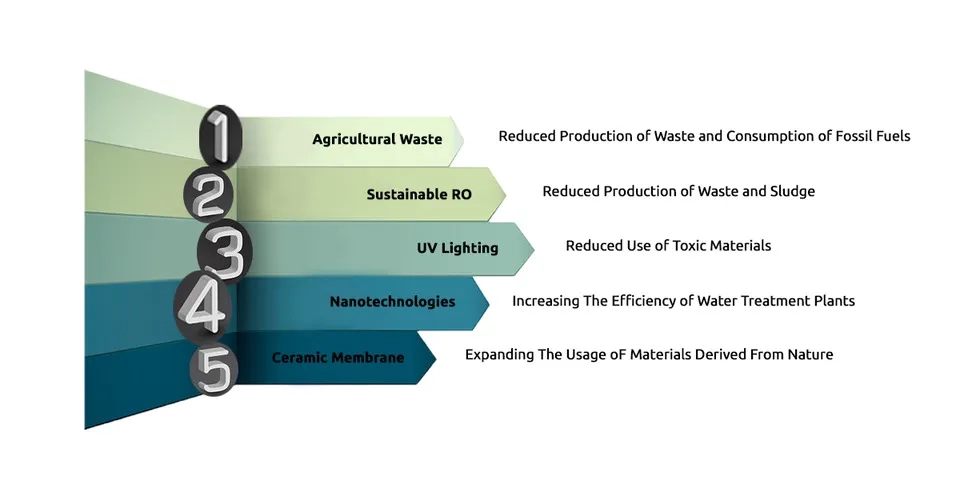
To achieve sustainability in water treatment, various techniques have been developed. One of the most recent sustainable practices involves the utilization of agricultural waste for water treatment, which has a minimal environmental footprint compared to conventional methods. Furthermore, innovative approaches in membrane science, particularly in Reverse Osmosis (RO), aim to embrace all aspects of sustainability from the perspective of the circular economy. This circular economy approach seeks to reduce waste and prioritize the recycling of natural resources and materials. Other promising technologies for environmentally friendly water treatment include Ultraviolet (UV) techniques and nanotechnology. Additionally, the age-old technique of ceramic filtration has evolved to meet the demands of the contemporary world. This article will delve into an examination of these leading sustainable water treatment methods
1. Utilization of Agricultural Waste
The utilization of cost-effective adsorbents to reduce the expenses of water treatment processes has garnered increased attention in recent years. Natural agricultural waste materials, such as seeds, fruit peels, nut shells, crop residues, and fruit shells, serve as efficient and readily available adsorbents. The use of agricultural waste for treating contaminated water represents a simple and efficient method that effectively manages both waste and water, making it a top-choice approach (Hashtroudi. 2018).
Several methods for making use of agricultural waste, such as biomass, have been developed, including the use of biomass as a raw material for the fabrication of membranes and as a natural coagulant. Biomass materials are widely available, abundant, inexpensive, and have few secondary pollution problems, and they are also rich in carboxyl, amino, and hydroxyl groups, which are active functional groups for pollutant adsorption and chemical purification in water bodies. Despite the many benefits of biomass, certain limits of single biomass cannot be ignored, such as their limited adsorption capacity, low mechanical resistance and chemical instability (Shuping. 2022).
2. Sustainable Design of RO
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is widely recognized as the leading technology for potable water production in water treatment. Since its creation, RO has seen considerable advancements in the fields of material science, process improvement, system optimization, membrane production techniques, and modification. However, a key barrier to the successful implementation of this technique has been the trade-off between membrane permeability and salt rejection, as well as membrane fouling (Hailemariam et al. 2019).
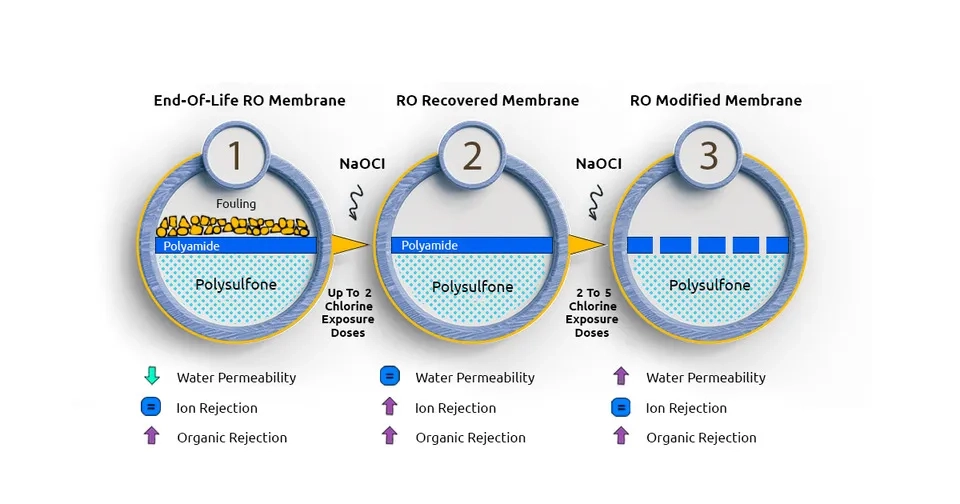
In recent years, efforts have been made to reduce the environmental impact of RO and promote sustainability in water treatment. Various practices have been proposed and studied to achieve this goal. Some of the latest sustainable approaches in RO for water treatment include the sustainable design of RO desalination with hybrid renewable energy systems, the surface modification of substrates and active layers of RO membranes, the reuse of membranes, and waste reduction through membrane antifouling approaches. Damaged RO membranes can also find new applications in membrane biofilm reactors or as support materials for recycled anion-exchange membranes, while RO membranes that have reached the end-of-life can be repurposed as ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes (Lejarazu-Larrañaga et al. 2019; Li et al. 2019).
3. UV Techniques
The necessity for acknowledging UV approaches as sustainable water treatment techniques was demonstrated through a comparative analysis of light-driven advanced oxidation processes. While UV techniques have minimal environmental impact, their biggest environmental concern is electricity consumption, which could be reduced by up to 87.5% through the use of renewable energy sources (Foteinis et al. 2018).
Currently, UV water treatment techniques utilize blacklight (UV-BL) lamps, which are energy-intensive, have a short lifespan, and contain toxic materials. The utilization of light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) can offer a more sustainable water treatment method. Generally, LEDs have 61% less environmental footprint than conventional techniques (McKee, Chatzisymeon. 2022)

4. Nanotechnology Application
Achieving sustainable water use will be based on a combination of factors, among which the efficient and responsible management of resources is paramount. In addition, water treatment technologies will provide a critical contribution. Nanomaterials hold significant potential for developing water purification methods. Due to their small size, nanomaterials can be used effectively for water purification and filtering. Specifically, nanomaterials may act as catalysts in oxidation processes for water treatment. Nanosensors are also under development for monitoring water treatment. (Pulizzi et al. 2018).
Despite the numerous advantages of nanomaterials-based techniques in water purification, careful consideration must be given to selecting the appropriate types of nanomaterials. Utilizing low-cost and non-toxic materials, such as chitosan and iron-based nanomaterials, can significantly contribute to achieving sustainability goals across various aspects of water treatment. Their environmentally friendly attributes make them promising candidates for advancing water purification practices further (Kamali et al. 2019).
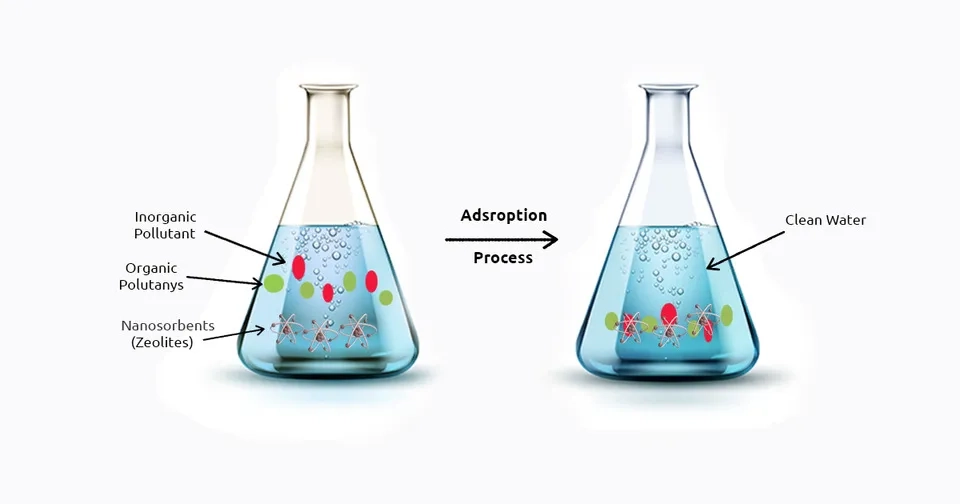
5. Ceramic Membranes
Water treatment involves various technologies, among which adsorption is considered a simple, effective, economical, and sustainable method. In recent years, ceramic membranes have developed into a new technology for water treatment. Ceramic membranes are favored because they have a longer life with less replacement and lower operational costs. Ceramic membranes are made up of inorganic materials and have shown extreme potential applications in tough conditions such as high temperatures, extreme pH values, etc. In the last decade, researchers have explored various types of low-cost ceramic membranes for water treatment applications (Latwal et al. 2023; Mukhopadhyay et al, 2019)
Despite the numerous advantages of nanomaterials-based techniques in water purification, careful consideration must be given to selecting the appropriate types of nanomaterials. Utilizing low-cost and non-toxic materials, such as chitosan and iron-based nanomaterials, can significantly contribute to achieving sustainability goals across various aspects of water treatment. Their environmentally friendly attributes make them promising candidates for advancing water purification practices further (Latwal et al. 2023).
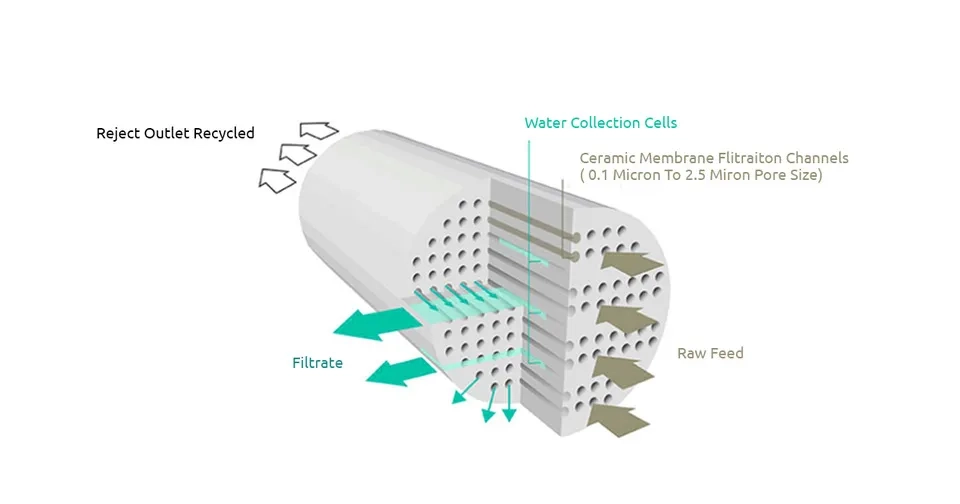
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, the development of sustainable water treatment methods is a multifaceted challenge that necessitates careful evaluation of social, economic, and environmental considerations. Various approaches have emerged as top practices in achieving sustainable water purification, encompassing waste reduction, utilization of natural resources, and enhanced efficiency of water treatment plants. Among these, the utilization of agricultural waste, the design of sustainable reverse osmosis systems, the adoption of ceramic membranes, and the application of UV and nanotechnologies have proven particularly effective in promoting environmentally friendly and resource-efficient water treatment processes. Embracing these innovative methods is crucial in safeguarding our water resources for future generations.
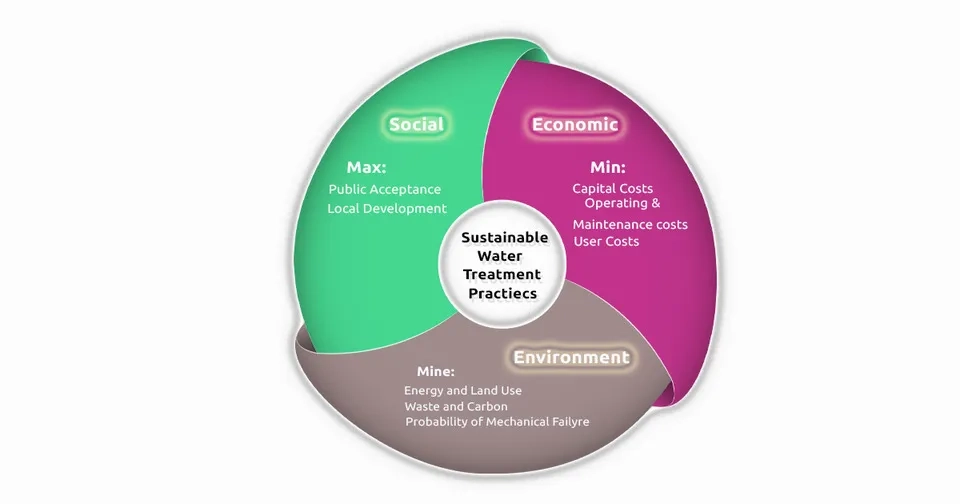
The development of conventional modeling methods, whether for process control or optimization, has primarily been driven by the need to achieve more favorable economic goals or reduce costs. It is unsustainable to design and simulate processes just with the intention of saving costs by using only economic restrictions. While keeping costs to a minimum, a sustainable modeling strategy should combine all factors, including technological, economic, environmental, and social restrictions. As a result of their capacity to optimize multi-objective models, AI approaches are recognized as sustainable techniques in water treatment (Yusuf et al. 2020).
AI tools have been widely used to optimize water treatment processes to obtain efficient performance. Indeed, automation has played a key role in redefining the issues of water treatment.AI has been developed as a versatile tool for data processing and optimizing intelligent water services while addressing issues of monitoring, management and labor costs. Recently, specific AI tools, such as artificial neural networks and genetic algorithms, have been implemented for self-monitoring and modeling applications for sustainable water treatment (Yuan et al. 2023).
