
Global warming is not an easy challenge to be neglected. According to new updates from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), in the next 5 years, our planet is going to experience the highest temperatures and break past records, resulting from the high concentration of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere and their heat-trapping property (WMO, 2023). This phenomenon not only affects the environment but also harms the lives of living things for a long period. So, everyone needs to be aware of the recent causes of global warming and help to mitigate them.
Global warming is a major environmental problem faced in the earth and its impacts affect the livelihood of all living beings. Global warming is happening due to industrialization, and the emission of carbon dioxide by human intervention (Sangam et al. 2019).
Global warming is defined as an increase in the average temperature of the Earth's atmosphere, especially a sustained increase great enough to cause changes in the world climate. The increase in carbon dioxide level is making the Earth's atmosphere hotter. Global warming causes a lot of climate changes in the atmosphere such as changes in weather patterns, changes in air circulation patterns, jet stream, rain without season, melting ice caps, declining ozone layer, the occurrence of heavy storms, cyclones, floods, epidemic diseases, lack of food and so many effects. Its threatening effects are increasing day by day and creating danger for human life (IPCC, 2022). It has become one of the subjects of big social issues that need individual social awareness to a great level. There are many causes of global warming, some are natural causes, and others are human-made causes. The most important cause of global warming is greenhouse gasses which are generated by some natural processes as well as human activities (Newton et al., 2019).
Since global warming is a hot topic, most researchers, academicians, and others concentrate more on this particular topic for their study. Therefore, the present study has been undertaken to indicate the top 8 causes of global warming and their effects on climate change.

1. Eight Causes of Global Warming
Global warming is mainly caused by increasing Greenhouse Gasses (GHGs) concentrations including, water vapor, methane, ozone, carbon dioxide, Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), and nitrous oxide (Venkataramanan, 2011). The greenhouse effect is the main criterion of the earth being a suitable place to live, without GHGs, the surface temperature of the earth would be too low and cold therefore, the earth would not be a place to live on. Although, the increase in the amount of GHGs in the atmosphere causes this dangerous phenomenon for the climate, that is, global warming (Anderson et al., 2016). As it is needed to know how this phenomenon takes place, in the following paragraphs, 8 recent causes of global warming will be explained.
1.1. Burning of Fossil Fuels
Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of global warming due to the greenhouse gasses it emits, primarily carbon dioxide, then methane and other greenhouse gasses. Here is an explanation of how this process contributes to climate change:
Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas contain high amounts of carbon. When they are burned for energy, chemical reactions release CO2 as a byproduct into the atmosphere. CO2 is a greenhouse gas, meaning it absorbs and re-emits infrared radiation from the sun, trapping heat in the atmosphere. Higher CO2 levels cause more heat to be retained, increasing surface temperatures on Earth. Before industrialization, CO2 levels were around 280 parts per million for about 6000 years. But in 2022, it was 421 ppm, a 50% increase in less than a century (NOAA, 2022). The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change estimates that fossil fuel burning accounts for over 75% of the total human-caused CO2 emissions between 1970 and 2010 (IPCC, 2013). When fossil fuels are burned for electricity generation, transportation, industrial processes, home heating, etc., billions of tons of CO2 are emitted every year. Much of the CO2 stays in the atmosphere for centuries.
The result is a greenhouse effect that warms the planet above natural levels, causing global warming and related climate change impacts.

1.1.1. Industrial Processes
Even though industrialization has been proven harmful to the environment and affects climate change, it is still a route to prosperity and greater quality of life. But the problem is, people should adapt themselves to warmer temperatures, extremes of weather, and changes in beliefs and ways of life. Considering these challenges, the impact of climate change must be taken into account in industrialization. In particular, an account should be taken of the significant impacts on the environment caused by changing people's behavior and values (Mgbemene et al., 2016).
1.1.2. Transportation
Burning fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel releases carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. The buildup of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses like methane, nitrous oxide, and hydrofluorocarbons is causing the Earth's atmosphere to warm, resulting in changes to the climate we are already starting to see today. Approximately 30% of total greenhouse gas emissions were from transportation between 1990 to 2021 in the U.S. which indicates that GHG emissions in the transportation sector have increased more compared to other sectors (EPA, 2022).

1.1.3. Power Generation
Generating power via fossil fuels results in high greenhouse gasses emission. As the population grows, more power energy must be generated to activate essential sectors such as industry, and run appliances and devices. This demand for generating power raises greenhouse gasses concentration and becomes a reason for global warming. The solution for this problem is to replace fossil fuels with renewable energy sources such as wind to generate power (Vargas et al., 2019; Das and Sharma, 2023).

1.2. Livestock Farming
The growth of population and income in addition to urbanization, causes a rapid rise in livestock farming demands. Simultaneously, livestock farming is facing increasing pressure from global warming, more variable precipitation patterns, more frequent extreme events, and increasing carbon dioxide concentrations. It is found that Such changes have affected livestock performance; according to Predictive models, the impacts are mostly negative (Scarcha et al, 2018). Meanwhile, livestock farming is a direct source of both methane and nitrous oxide and an indirect source of those gasses and carbon through land use and feed production. Globally, the livestock farming emissions share is an estimated 14.5% of total human-caused greenhouse gas emissions (Gerber et al, 2013); which is the main contributor to increasing climate change and global temperature rise. The interaction between ongoing global warming and increasing livestock production demand makes it challenging to increase production as well as controlling climate impacts and GreenHouse Gas (GHG) emissions (Cheng et al, 2022).

1.3. Land Use Change
Changes in land use have a large impact on the Earth's surface and greenhouse gas concentrations, which both are related to global warming. As a result of human activities like deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion, land use patterns significantly have changed. Urbanization and the transformation of natural landscapes into impermeable surfaces not only affect ecosystems but also reduce the capacity of the land to store carbon. Due to the buildup of greenhouse gasses brought on by these modifications in land use, the greenhouse effect is amplified and causes global warming (IPCC, 2022).
1.3.1. Deforestation
Forests cover about 30% of the Earth's land surface. As forests grow, their trees take in carbon from the air and store it in wood, plant matter, and under the soil. If not for forests, much of this carbon would remain in the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas driving climate change. Each year since 2000, forests are estimated to have removed an average of 2 billion metric tons of carbon from the atmosphere (Lejeune et al., 2018). This "carbon sink function" of forests is slowing climate change by reducing the rate at which CO2, mainly from fossil fuel burning, builds up in the atmosphere. Careful forest management can therefore be an important strategy to help address climate change in the future. Healthy forests also provide a host of other benefits, from clean water to habitat for plants and animals that can live nowhere else (Lesiv et al.. 2022). For example, the southern Amazon is one of the fastest-changing places on earth due to deforestation. According to researchers, the size of deforested lands and different land uses affect the ecosystem and local climate; therefore, alternative agricultural practices and forest restoration are needed to mitigate local climate change and maintain ecosystem conditions (Maeda et al., 2021).

1.3.2. Urbanization
Urbanization significantly impacts global warming through various mechanisms that increase greenhouse gas emissions and alter the Earth's climate. As cities expand and populations concentrate in urban areas, energy demands rise, leading to higher fossil fuel consumption and subsequent carbon dioxide emissions. Additionally, urban centers generate substantial vehicular traffic, contributing to elevated levels of CO2 and other pollutants (Ren et al.. 2020). The phenomenon of the urban heat island effect exacerbates local warming, as concrete and asphalt replace natural surfaces, absorbing and retaining heat. Furthermore, land use changes associated with urbanization, such as deforestation and ecosystem disruption, reduce carbon sinks and hinder the planet's ability to sequester CO2. Waste generation in cities also leads to the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas (Seto et al.. 2012).

1.3.3. Agricultural Practices
The agricultural sector, which accounts for about 24% of total anthropogenic emissions, has the potential to contribute to total greenhouse gas emissions, and the world population growth is expected to sustain high levels of agricultural production in order to fulfill food demands. Meanwhile, there is huge potential for carbon sinks in this sector, such as land-use change. Over the past 40 years, there has been remarkable evidence that the collection of greenhouse gases in the upper atmosphere drives climate change, especially rising temperatures. The average surface temperature of the Earth had increased by 0.6 ± 0.2 °C in the 20th century and is supposed to increase by 0.3 to 2.5 °C over the next 50 years (IPCC, 2007).
Agriculture can be a source and sink of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. It is the source of three major greenhouse gasses like CO2, N2O, and CH4. There are two major sources of anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gasses from agriculture; first, energy consumption in agriculture for the production and use of agricultural materials and machinery, second, the management of farmlands. As a result, mitigation methods are needed to reduce emissions from this sector, so that agricultural communities can act and measure their progress (Lenka, et al., 2015).

1.4. Population Growth
Population growth has a significant impact on global warming due to its influence on different factors, such as energy consumption, resource demands, and greenhouse gas emissions. As the global population increases, the demand for energy to power homes, industries, and transportation systems increases as well (Mikhaylov et al., 2020). This heightened energy consumption leads to higher carbon dioxide emissions from burning fossil fuels, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming. In addition, a larger population requires more resources, leading to deforestation, land use changes, and increased agricultural practices, all of which release additional greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere (Weber et al., 2019).
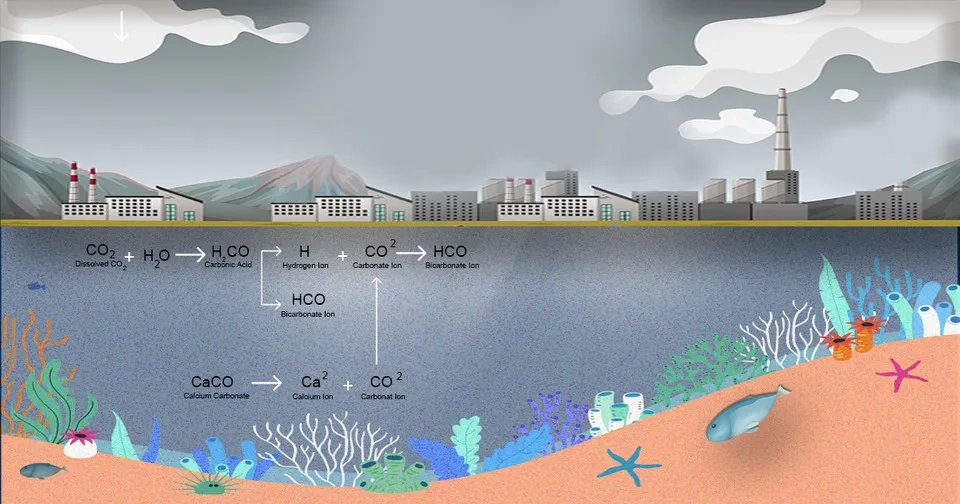
1.5. Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is one of the main results of rising atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, and it has considerable effects on global warming. The saltwater becomes more acidic as a result of the oceans absorbing a significant amount of the extra CO2, released by humans, into the atmosphere. This process, which has negative impacts on ocean ecosystems, affects the ability to form and maintain calcium carbonate structures in organisms like corals, mollusks, or plankton. Furthermore, ocean acidification is affecting global warming because it could result in the release of more CO2 from marine animals and sediments which are likely to increase the greenhouse effect (Feely et al., 2009).
1.6. Landfills and the Methane Release Problem
Landfills and methane release are significant contributors to global warming, as they play a crucial role in greenhouse gas emissions. When organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, decomposes in landfills without access to oxygen, it produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas that is approximately 25 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide over 100 years (Bian et al., 2022). As methane is released into the atmosphere, it contributes to the greenhouse effect, leading to higher global temperatures and climate change. Addressing the landfill and methane release problem is crucial for effective climate change mitigation strategies (Bo-Feng et al., 2014).

1.7. Permafrost Thaw
There is a huge amount of carbon stored in permafrost which probably is twice as much as the atmosphere contains. This carbon is the residual plants and other organic matter that didn’t fully decompose in the frozen soils over thousands of years (Schuur et al., 2015). When the permafrost thaws, bacteria will break down organic matter and release their carbon into the atmosphere as greenhouse gasses. The greenhouse gasses are mainly carbon dioxide and methane. Once these greenhouse gasses get to the atmosphere, their heat trapping property starts to warm the atmosphere and increase its temperature which results in creating a positive feedback loop that thaws more permafrost. There are a lot of global warming loops due to past emissions; this means, permafrost will keep thawing even if greenhouse gas emissions were stopped. But by making essential efforts to curb emissions, the trend of permafrost thawing will slow down (Randers et al,, 2020).

1.8. Melting Ice and Snow
As the reflective ice and snow surfaces reduce, the earth starts to absorb more heat and reflects less solar energy. This property, which is called albedo, has a significant impact on climate and environmental change, especially in global warming. Water, ice, and snow are associated with each other and can be converted to each other with changes in temperature and weather. Due to global warming, ice and snow sources have melted and the extent of snow cover and sea ice has declined. In addition, the sea level has risen as well. All these changes result in global surface albedo reduction followed by global atmosphere temperature rise (Zhang et al., 2022).
2. Conclusion
In conclusion, today's top 8 causes of global warming include a diverse range of human activities that collectively contribute to the growth of the greenhouse effect. These main worldwide causes which were discussed in this study include, the burning of fossil fuels for energy production and transportation, deforestation and land use changes that reduce carbon sinks, industrial processes emitting greenhouse gasses, and methane emissions from agriculture. Additionally, urbanization and the urban heat island effect, as well as increasing livestock production, contribute to raised levels of greenhouse gasses. Lastly, permafrost thawing and melting snow which indicate global warming loops showed the importance of greenhouse gas emission rate. A comprehensive and coordinated effort from governments, businesses, and individuals is crucial to transition towards sustainable practices and reduce our carbon footprint, safeguarding the planet for a more sustainable future.